GSC2 / YGR032W
Protein
Protein abundance data, domains, shared domains with other proteins, protein sequence retrieval for
various strains, sequence-based physico-chemical properties, protein modification sites, and external
identifiers for the protein.
Protein abundance data, domains, shared domains with other proteins, protein sequence retrieval for various strains, sequence-based physico-chemical properties, protein modification sites, and external identifiers for the protein.
AlphaFold Protein Structure
AlphaFold, developed by DeepMind, is an AI program that accurately predicts protein structures from amino acid sequences, enabling visualization of protein conformations. The predicted structures can be accessed through the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and AlphaFold Protein Structure Database.
Experimental Data
Contains experimentally-derived protein half-life data obtained using stable isotope labeling by amino acids (SILAC) coupled with mass spectrometry. This section also contains protein abundance data for both untreated and treated cells obtained from over 20 studies. These data have been normalized and converted to a common unit of molecules per cell.
Protein Half Life
Increase the total number of rows showing on this page by using the pull-down located below the table, or use the page scroll at the table's top right to browse through its pages; use the arrows to the right of a column header to sort by that column; filter the table using the "Filter" box at the top of the table.
| Evidence ID | Analyze ID | Gene | Gene Systematic Name | Experiment | Result | Reference |
|---|
Protein Abundance
Increase the total number of rows showing on this page by using the pull-down located below the table, or use the page scroll at the table's top right to browse through its pages; use the arrows to the right of a column header to sort by that column; filter the table using the "Filter" box at the top of the table.
| Evidence ID | Analyze ID | Gene | Gene Systematic Name | Abundance (molecules/cell) | Media | Treatment | Treatment time | Fold Change | Visualization | Strain background | Original Reference | Reference |
|---|
Domains and Classification - S288C
Collection of computationally identified domains and motifs, as determined by InterProScan analysis; includes protein coordinates for the domain, a domain Description, a Source and corresponding accession ID, and the number of S. cerevisiae genes that share the same domain.
Increase the total number of rows showing on this page by using the pull-down located below the table, or use the page scroll at the table's top right to browse through its pages; use the arrows to the right of a column header to sort by that column; filter the table using the "Filter" box at the top of the table.
| Evidence ID | Analyze ID | Gene | Gene Systematic Name | Protein Coordinates | Accession ID | Description | Source | No. of Genes with Domain |
|---|
Domain Locations
Visual representation of the locations of the domains within the protein, as listed in the Domains and Classification table. Each row displays the domain(s) derived from a different Source, with domains color-coded according to this Source.
Scroll over a domain to view its exact coordinates and its Description.
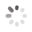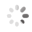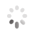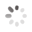
Alleles
Curated mutant alleles for the specified gene, listed alphabetically. Click on the allele name to open the allele page. Click "SGD search" to view all alleles in search results.
View all GSC2 alleles in SGD search
Sequence
Protein sequence for the given gene in S288C and other strains, when available. Use the pull-down menu under "Strain" to select the sequence for a specific strain. The displayed sequence can be downloaded in FASTA format as a .txt file. Amino acids displayed in blue represent modification sites. More detailed evidence for these modification sites is presented in the Post-translational Modifications table, located just below the protein sequence.
This locus is not translated into a protein.
* Blue amino acids indicate modification sites. More information below.
Post-translational Modifications -
Modification sites for the protein in the selected strain, based on the presence of a residue in the specific strain, as inferred from experimental evidence.
Increase the total number of rows showing on this page by using the pull-down located below the table, or use the page scroll at the table's top right to browse through its pages; use the arrows to the right of a column header to sort by that column; filter the table using the "Filter" box at the top of the table.
| Site | Modification | Modifier | Source | Reference |
|---|
Sequence-Based Physico-chemical Properties - S288C
Calculated protein properties, including amino acid composition, length, coding region calculations, and atomic composition.
Amino Acid Composition
Sort table using the arrow to the right of a column header to sort by that column; download all properties as a .txt file using the "Download Properties" button.
| Amino Acid | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|
Physical Details
| Length (a.a): | |
| Molecular Weight (Da): | |
| Isoelectric Point (pl): | |
| Formula: | |
| Aliphatic Index: | |
| Instability Index: |
Coding Region Translation Calculations
| Codon Bias: | |
| Codon Adaptation Index: | |
| Frequence of Optimal Codons: | |
| Hydropathicity of Protein: | |
| Aromaticity Score: |
Extinction Coefficients at 280nm
| ALL Cys residues appear as half cystines: | |
| NO Cys residues appear as half cystines: |
Atomic Composition
Sort table using the arrow to the right of a column header to sort by that column; download all properties as a .txt file using the "Download Properties" button.
| Atom | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|
Data not found or not available for
External Identifiers
List of external identifiers for the protein from various database sources.
Increase the total number of rows showing on this page by using the pull-down located below the table, or use the page scroll at the table's top right to browse through its pages; use the arrows to the right of a column header to sort by that column; filter the table using the "Filter" box at the top of the table.
| Alias ID | External ID | Source |
|---|
Resources
Homologs
AGD | AnalogYeast | BLASTP at NCBI | CGD | FungiDB | PhylomeDB | PomBase | PomBase | PomBase | PomBase | YGOB | YOGY
Protein Databases
AlphaFold Protein Structure | GPMDB | ModelArchive | Pfam domains | SUPERFAMILY | TopologYeast | UniProtKB
Localization
CYCLoPs | dHITS | LibrarYeast | LoQAtE | YeastGFP | YeastRGB | YPL+